Ecg Wave Form
Ecg Wave Form - This type of ecg is conducted for 24 hours. The standard calibration is 10 mm (10 small boxes), equal to 1 mv. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. Different types of waves produced by electrocardiogram. 1 mm = 0.1 mv; Ordinate) as a function of time (sec; Web an electrocardiogram (ecg or ekg) is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity as a graph over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body. P duration < 0.12 sec p amplitude < 2.5 mm A standard 12 lead ecg is shown in [figure 1]. Web the goal of the electrocardiogram interpretation is to determine whether the ecg waves and intervals are normal or pathological.
Waveformecg extracts and stores information from ge and philips file headers, including analysis results. Web the best selection of royalty free ecg waves vector art, graphics and stock illustrations. The pr interval, the pr… The standard calibration is 10 mm (10 small boxes), equal to 1 mv. This type of ecg is conducted for 24 hours. It is used to record the electrical activity of the heart from different angles to both identify and locate pathology. This electrical wave causes the. Web analyses of ecgs can provide information on the heart’s both normal and pathological functions. Web an electrocardiogram (ecg or ekg) is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity as a graph over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body. Web the goal of the electrocardiogram interpretation is to determine whether the ecg waves and intervals are normal or pathological.
Abscissa) measured over a single heartbeat. Web how can we interpret a waveform? Different portions of the ecg waveform are influenced differently. This test is used to measure ecg when you are on an exercise bike. Web there are three main components to an ecg: Electrodes are placed on different parts of a patient’s limbs and chest to record the electrical activity. Web the heart's electrical activity is represented on the monitor or ecg tracing by three basic waveforms: This electrical wave causes the. Web the classical ecg curve with its most common waveforms. P duration < 0.12 sec p amplitude < 2.5 mm
The ECG Waveform (UK/USMLE) PostGradMedic YouTube
It is used to record the electrical activity of the heart from different angles to both identify and locate pathology. Web the classical ecg curve with its most common waveforms. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. The qrs waveform is influenced principally by ventricular muscle mass but may be influenced by differences in ventricular.
Heart activity during an ECG wave [40] Download Scientific Diagram
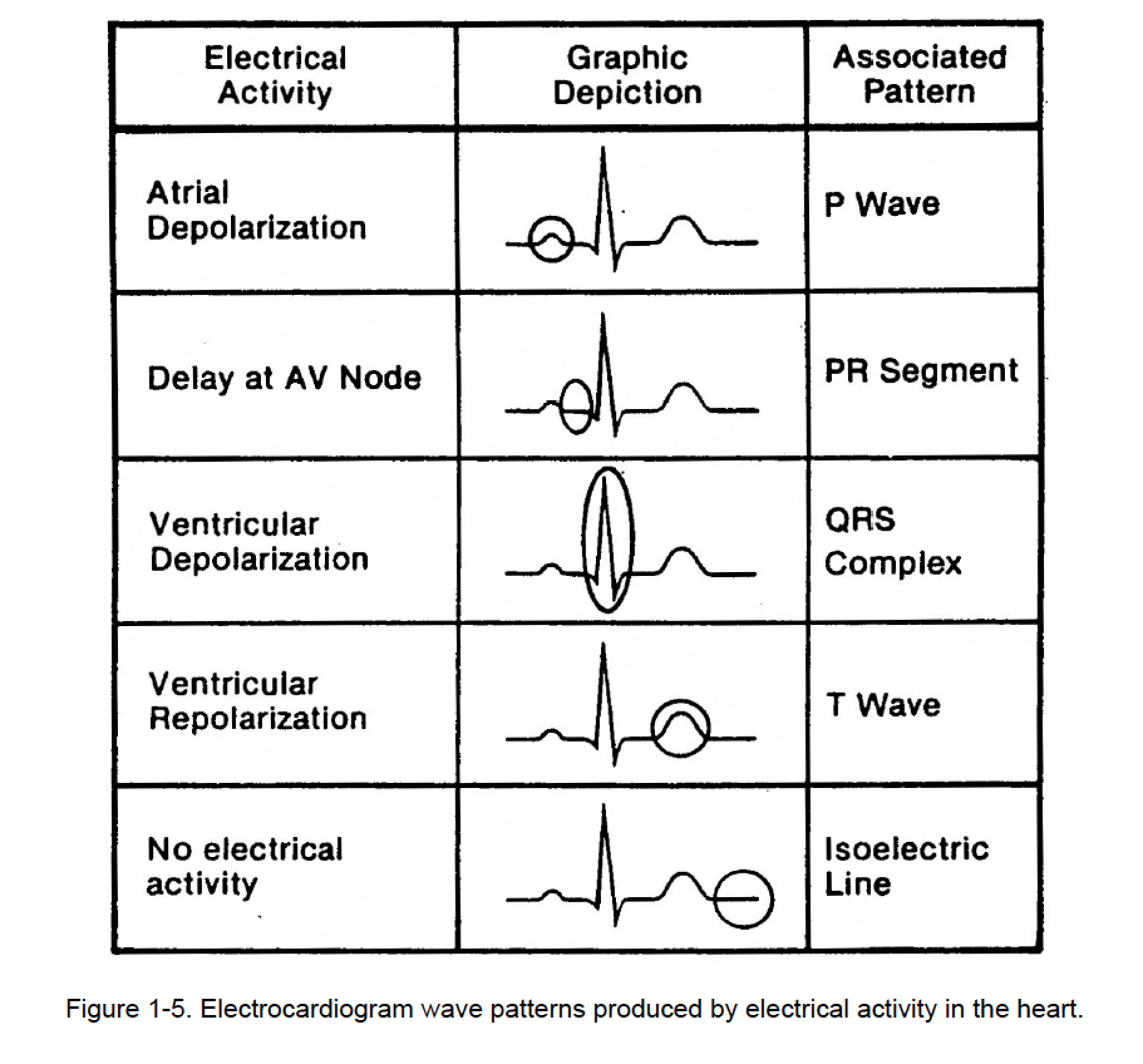
This electrical wave causes the. The qrs waveform is influenced principally by ventricular muscle mass but may be influenced by differences in ventricular filling which occur with cardiac failure or transiently with cord compression. Ordinate) as a function of time (sec; Web the heart's electrical activity is represented on the monitor or ecg tracing by three basic waveforms: The p.
Intro to EKG Interpretation Waveforms, Segments, and Intervals
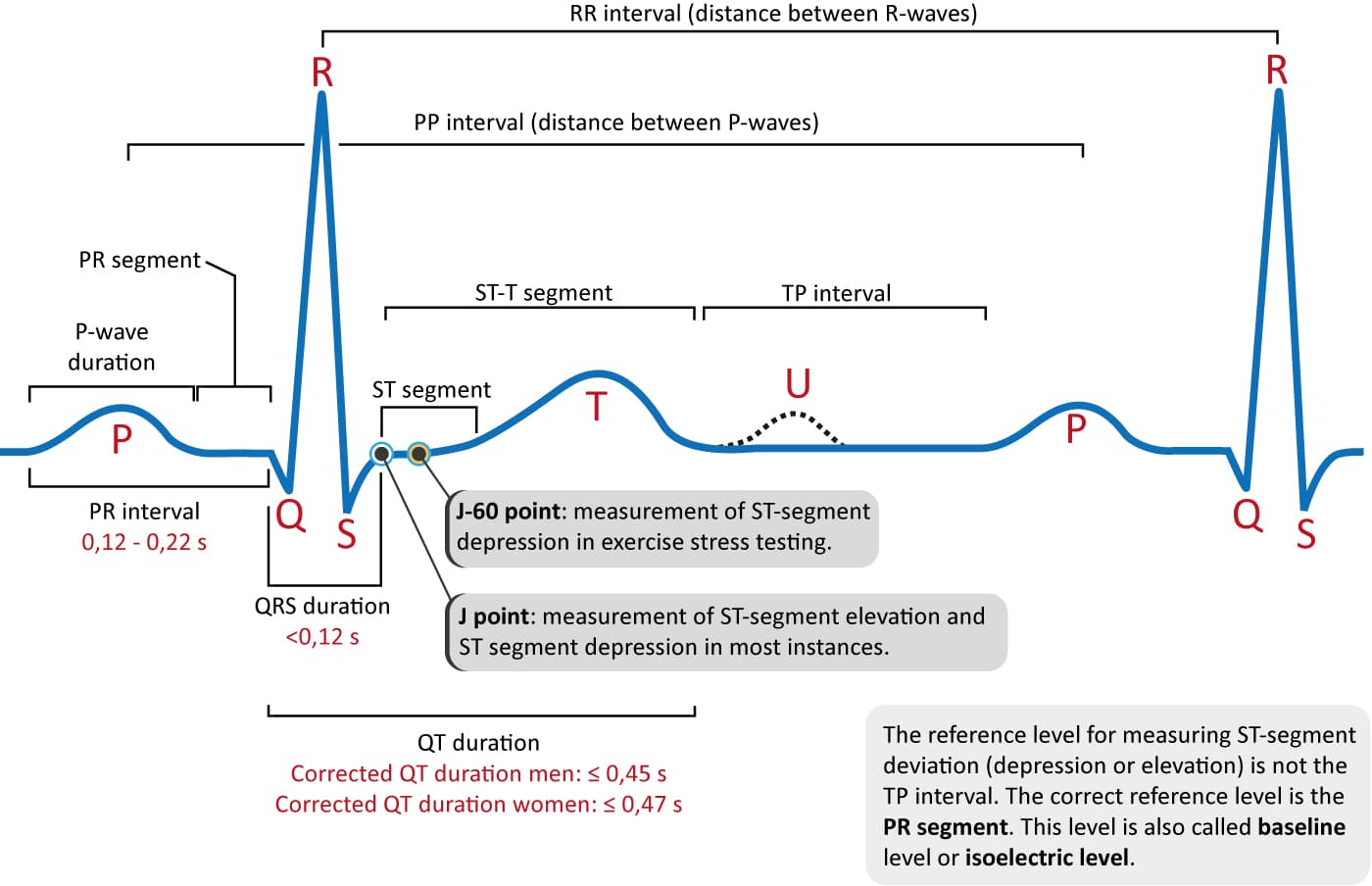
The p wave, which represents depolarization of the atria; This prevalent test can give emts, paramedics, nurses and doctors the ability to assess the heart's. P duration < 0.12 sec p amplitude < 2.5 mm These signals are transmitted to produce a record of cardiac activity. An ekg uses electrodes attached to the skin to detect electric currents moving through.
The Normal ECG The Student Physiologist
Electrical signal interpretation gives a good approximation of heart pathology. And the t wave, which represents repolarization of the ventricles. Web analyses of ecgs can provide information on the heart’s both normal and pathological functions. In order to successfully read an ekg, you must first understand the basics of an ekg waveform. Reading an ecg or ekg can be a.
105. GRAPHIC DISPLAY OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (C) Cardiac Rhythm
Users can browse their files, and upload ecg data in ge muse xml versions 7+, philips ecg xml versions 1.03+, and waveform database (wfdb) format. This electrical wave causes the. Ordinate) as a function of time (sec; The graph can show the heart’s rate and rhythm. Web an electrocardiogram — abbreviated as ekg or ecg — measures the electrical activity.
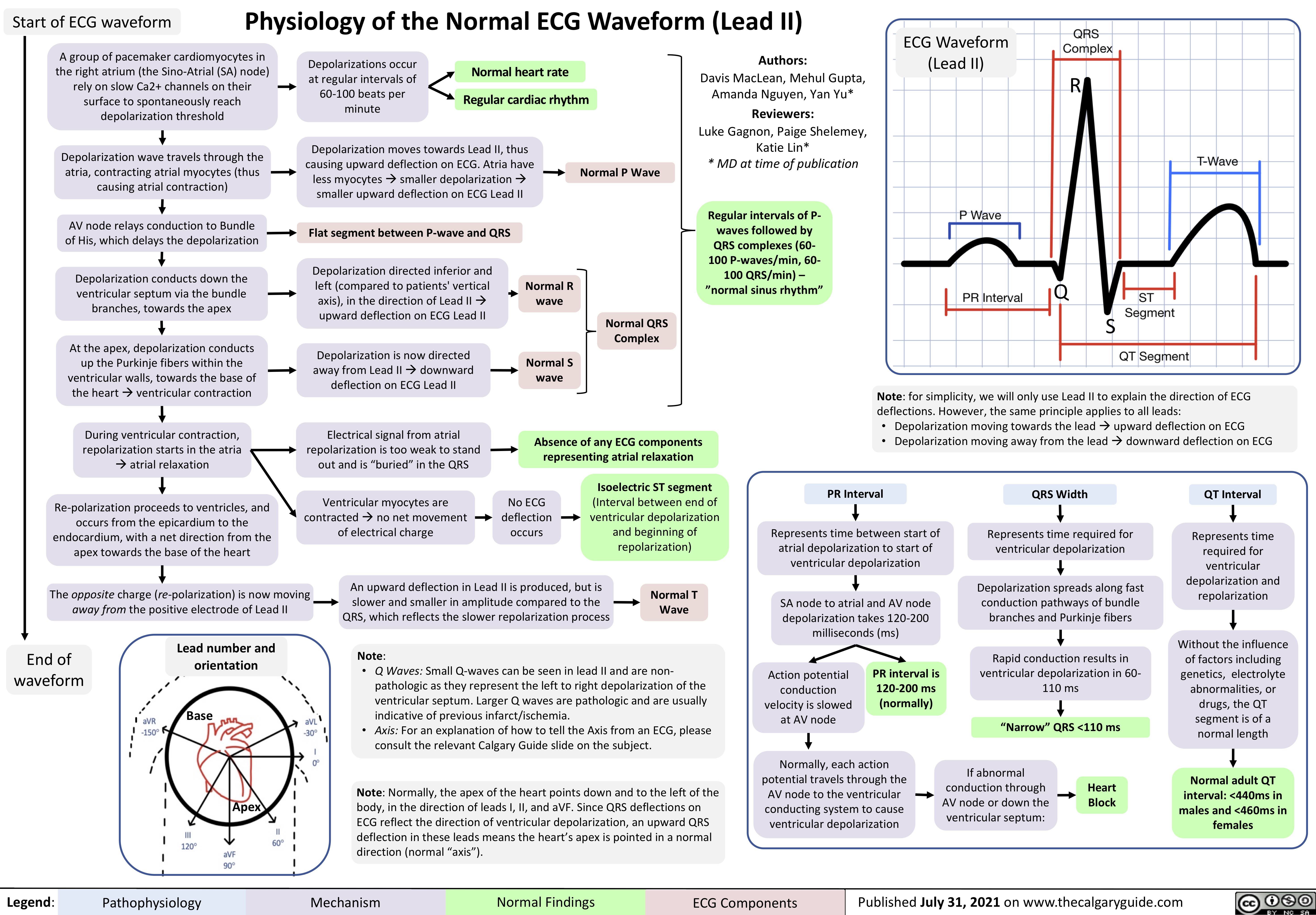
Physiology of the Normal ECG Waveform (Lead II) Calgary Guide
Ecg is the abbreviated term for an electrocardiogram. The ebook and accompanying lectures and tests covers all aspects of clinical ecg interpretation. A u wave is sometimes present. In order to successfully read an ekg, you must first understand the basics of an ekg waveform. How to read and interpret electrocardiograms (ecg/ekgs) is an important skill to have.
Image of one complete ECG waveform Download Scientific Diagram
When the wave forms are very large, half standard may be used (5 mm. Web one of the most useful and commonly used diagnostic tools is electrocardiography (ekg) which measures the heart’s electrical activity as waveforms. Different types of waves produced by electrocardiogram. Different portions of the ecg waveform are influenced differently. Reading an ecg or ekg can be a.
Overview of the ECG Waves, Deflections, Intervals, Durations ECG & ECHO
With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. Waveformecg extracts and stores information from ge and philips file headers, including analysis results. And the t wave, which represents repolarization of the ventricles. Web the heart's electrical activity is represented on the monitor or ecg tracing by three basic waveforms: This type of ecg is conducted for.
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog ST Elevation and Positive Troponin. Is it STEMI
The best way to interpret an ecg is to read it systematically: In order to successfully read an ekg, you must first understand the basics of an ekg waveform. P duration < 0.12 sec p amplitude < 2.5 mm With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. The ecg p, q, r, s, and t waves.
Normal Ecg Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
Electrical signal interpretation gives a good approximation of heart pathology. Web the heart's electrical activity is represented on the monitor or ecg tracing by three basic waveforms: Ecg interpretation requires knowledge of these waves and intervals. When the wave forms are very large, half standard may be used (5 mm. Web the goal of the electrocardiogram interpretation is to determine.
Web Analyses Of Ecgs Can Provide Information On The Heart’s Both Normal And Pathological Functions.
How to read and interpret electrocardiograms (ecg/ekgs) is an important skill to have. Web one of the most useful and commonly used diagnostic tools is electrocardiography (ekg) which measures the heart’s electrical activity as waveforms. These signals are transmitted to produce a record of cardiac activity. The lead v3 ecg waveform in shows body surface potential (uv;
This Type Of Ecg Is Conducted For 24 Hours.
Ecg sinusoidal pulse lines frequency heartbeat vector; With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. The ecg p, q, r, s, and t waves are labeled. Ordinate) as a function of time (sec;
This Test Is Used To Measure Ecg When You Are On An Exercise Bike.
1 mm = 0.1 mv; Heartbeat ecg electrocardiogram graph wave vector; The pr interval, the pr… Ecg is the abbreviated term for an electrocardiogram.
Web The Heart's Electrical Activity Is Represented On The Monitor Or Ecg Tracing By Three Basic Waveforms:
The heart’s electrical impulses are measured by a device called the holter monitor. P duration < 0.12 sec p amplitude < 2.5 mm Electrodes are placed on different parts of a patient’s limbs and chest to record the electrical activity. On occasion, particularly when the waveforms are small, double standard is used (20 mm equals 1 mv).