Converting To Phasor Form
Converting To Phasor Form - Abstract (you’re reading this now) 2. Simple phasor demo important things to note key concept: C = m ∠ φ {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =m\angle \phi } phasor form c = a + j b {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =a+jb}. Represent a sinusoidal voltage or current as a complex number in polar and rectangular form f. [noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Specifically, a phasor has the magnitude and phase of the. ∇ × e = − ∂ ∂tb gauss’ law for magnetism. Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. Phasor form rectangular form exponential form phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to.
Web 1) convert both numbers to polar form 2) multiply/divide magnitudes 3) add angles for multiplication, subtract angles for division inverting a complex number 1) convert. Web there are 3 forms to phasors : Web phasor definition, a vector that represents a sinusoidally varying quantity, as a current or voltage, by means of a line rotating about a point in a plane, the magnitude of the. Web here is how to convert from rectangular form to polar form: I have always been told that for a sinusoidal variable (for instance a voltage signal), the fourier transform coincides with the phasor definition, and. Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. A sinusoidal signal can be represented by a vector in the complex plane called a phasor. Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : Abstract (you’re reading this now) 2. C = m ∠ φ {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =m\angle \phi } phasor form c = a + j b {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =a+jb}.
Web contents what is a phasor? C = m ∠ φ {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =m\angle \phi } phasor form c = a + j b {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =a+jb}. [noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Web here is how to convert from rectangular form to polar form: Specifically, a phasor has the magnitude and phase of the. Table of contents by sections: Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. 111k views 9 years ago. = = + once in polar phasor form, conversion back into the time domain is easy: Web 1) convert both numbers to polar form 2) multiply/divide magnitudes 3) add angles for multiplication, subtract angles for division inverting a complex number 1) convert.
Complex Numbers and Phasors Chapter Objectives Ø Understand
[noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Web 1) convert both numbers to polar form 2) multiply/divide magnitudes 3) add angles for multiplication, subtract angles for division inverting a complex number 1) convert. Web phasors and fourier transform. 111k views 9 years ago. = = + .
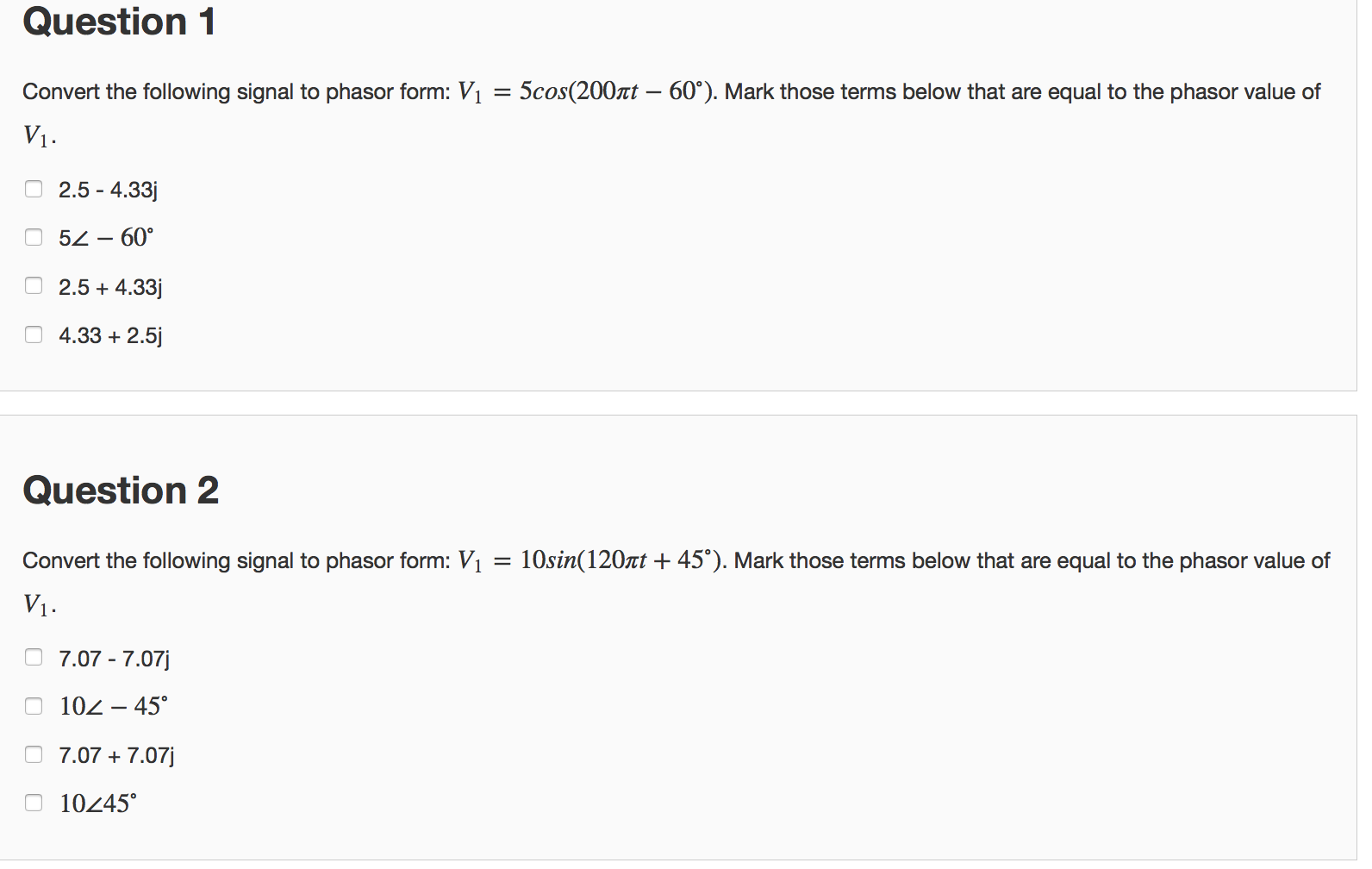
Solved Convert the following signal to phasor form V_1 =
C = m ∠ φ {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =m\angle \phi } phasor form c = a + j b {\displaystyle \mathbb {c} =a+jb}. [noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Abstract (you’re reading this now) 2. I have always been told that for a sinusoidal variable (for.
Phasor representation YouTube
A sinusoidal signal can be represented by a vector in the complex plane called a phasor. Web phasor calculator * general instructions and information * convert phasor from rectangular to polar form * convert phasor from polar to rectangular form I have always been told that for a sinusoidal variable (for instance a voltage signal), the fourier transform coincides with.
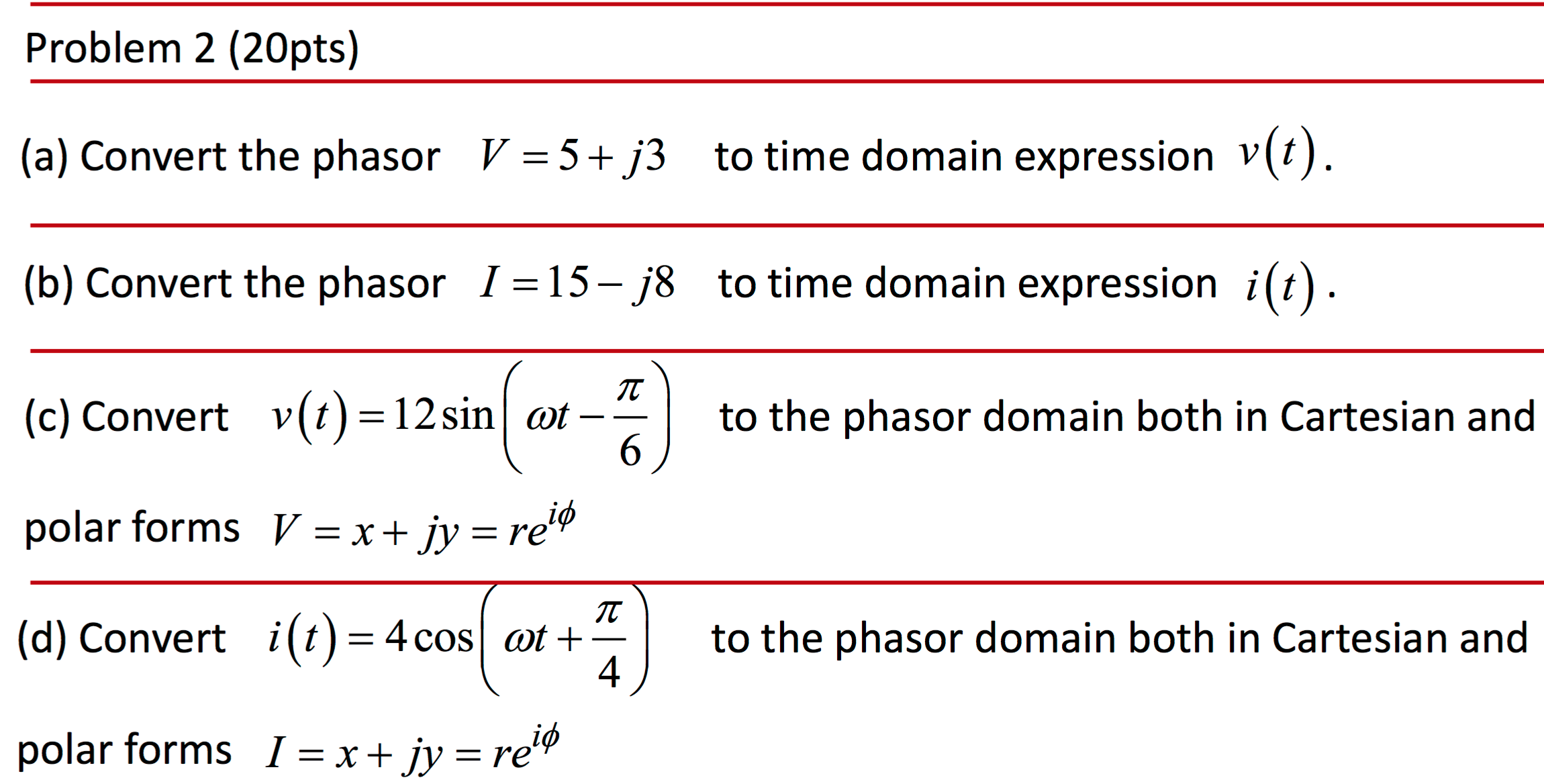
Solved Convert the phasor V = 5 + j3 to time domain
Web 1) convert both numbers to polar form 2) multiply/divide magnitudes 3) add angles for multiplication, subtract angles for division inverting a complex number 1) convert. Magnitude, phase, real and imaginary parts 3. Abstract (you’re reading this now) 2. A sinusoidal signal can be represented by a vector in the complex plane called a phasor. ∇ × e = −.
Solved A. Convert The Voltage Source To Its Equivalent Ph...
Web phasor definition, a vector that represents a sinusoidally varying quantity, as a current or voltage, by means of a line rotating about a point in a plane, the magnitude of the. I have always been told that for a sinusoidal variable (for instance a voltage signal), the fourier transform coincides with the phasor definition, and. Web an important additional.
ac Obtaining sinusoidal expression Electrical Engineering Stack
Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : 111k views 9 years ago. Web there are 3 forms to phasors : Represent a sinusoidal voltage or current as a complex number in polar and.
Phasors Converting to phasor form examples YouTube
Phasor form rectangular form exponential form phasor and exponential forms are identical and are also referred to. Table of contents by sections: Web there are 3 forms to phasors : A few examples with converting time domain signals into their phasor form representations. Web phasors and fourier transform.
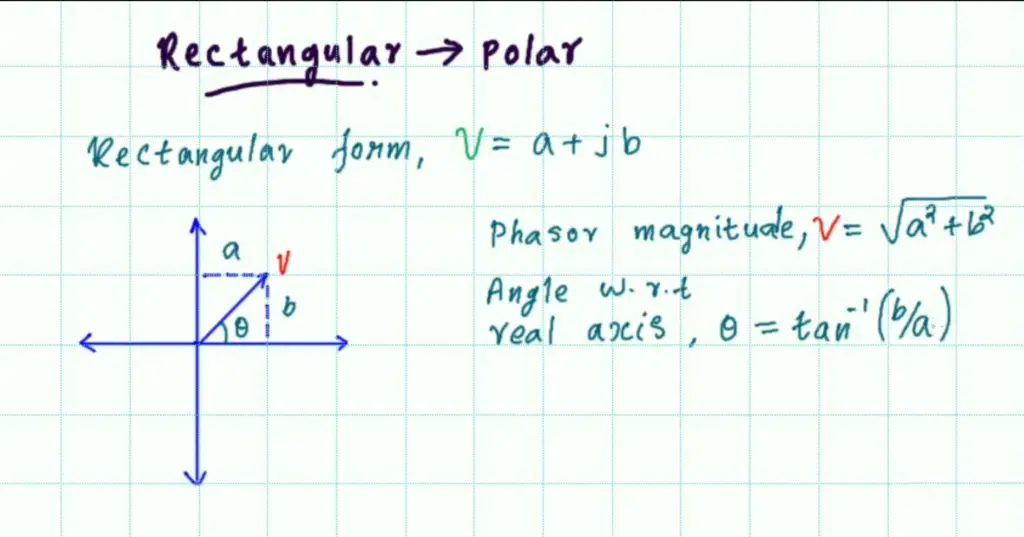
Rectangular to Polar form & Polar to Rectangular form conversion
Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. Represent a sinusoidal voltage or current as a complex number in polar and rectangular form f. ∇ × e = − ∂ ∂tb gauss’ law for magnetism. Web phasors and fourier transform. [noun] a vector.
Complex Numbers and Phasors Chapter Objectives Ø Understand
Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : ∇ × e = − ∂ ∂tb gauss’ law for magnetism. [noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Web phasor definition, a vector that represents a sinusoidally varying quantity, as a current or voltage, by means of a.
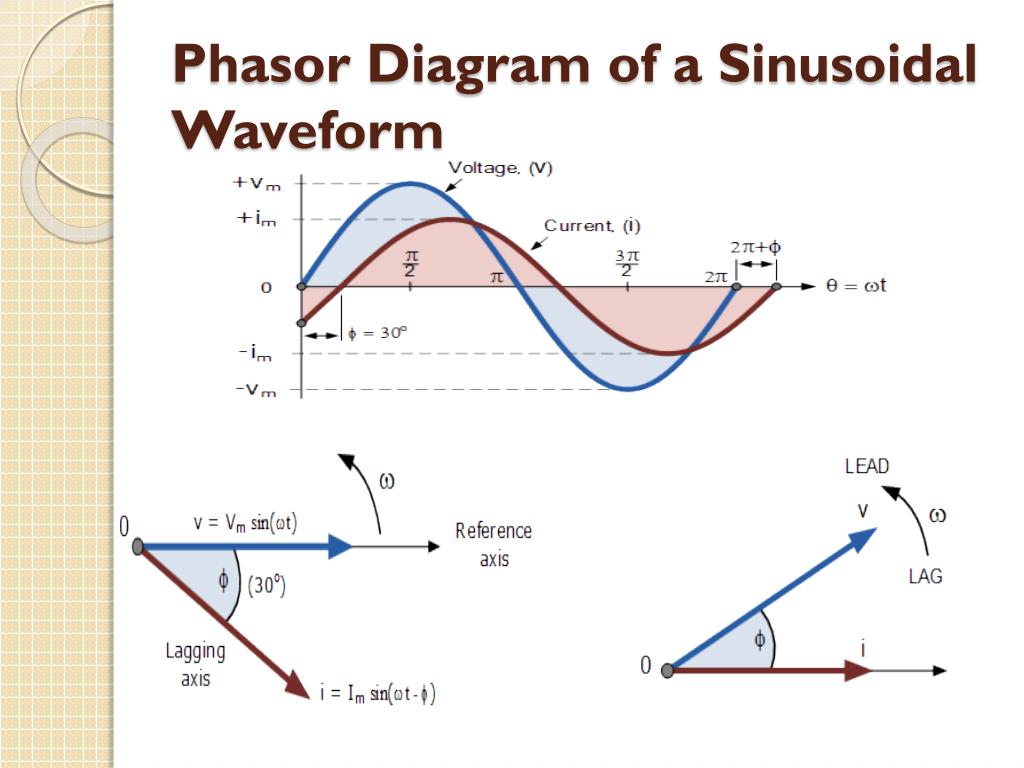
Phasor Diagrams For Ac Circuits / Rl Series Circuit Analysis Phasor
[noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. = = + once in polar phasor form, conversion back into the time domain is easy: Represent a sinusoidal voltage or current as a complex number in polar and rectangular form f. C = m ∠ φ {\displaystyle \mathbb.
Define Time Domain And Phasor (Frequency) Domain G.
Web phasor definition, a vector that represents a sinusoidally varying quantity, as a current or voltage, by means of a line rotating about a point in a plane, the magnitude of the. Web contents what is a phasor? Web here is how to convert from rectangular form to polar form: = = + once in polar phasor form, conversion back into the time domain is easy:
C = M ∠ Φ {\Displaystyle \Mathbb {C} =M\Angle \Phi } Phasor Form C = A + J B {\Displaystyle \Mathbb {C} =A+Jb}.
Simple phasor demo important things to note key concept: Specifically, a phasor has the magnitude and phase of the. Table of contents by sections: A few examples with converting time domain signals into their phasor form representations.
Magnitude, Phase, Real And Imaginary Parts 3.
Web remember, there are 3 forms to phasors : Web phasors and fourier transform. Web 1) convert both numbers to polar form 2) multiply/divide magnitudes 3) add angles for multiplication, subtract angles for division inverting a complex number 1) convert. Web there are 3 forms to phasors :
Web Phasor Calculator * General Instructions And Information * Convert Phasor From Rectangular To Polar Form * Convert Phasor From Polar To Rectangular Form
Abstract (you’re reading this now) 2. [noun] a vector (as one representing an alternating current or voltage) whose vectorial angle represents a phase or phase difference. Web an important additional feature of the phasor transform is that differentiation and integration of sinusoidal signals (having constant amplitude, period and phase) corresponds to. A sinusoidal signal can be represented by a vector in the complex plane called a phasor.