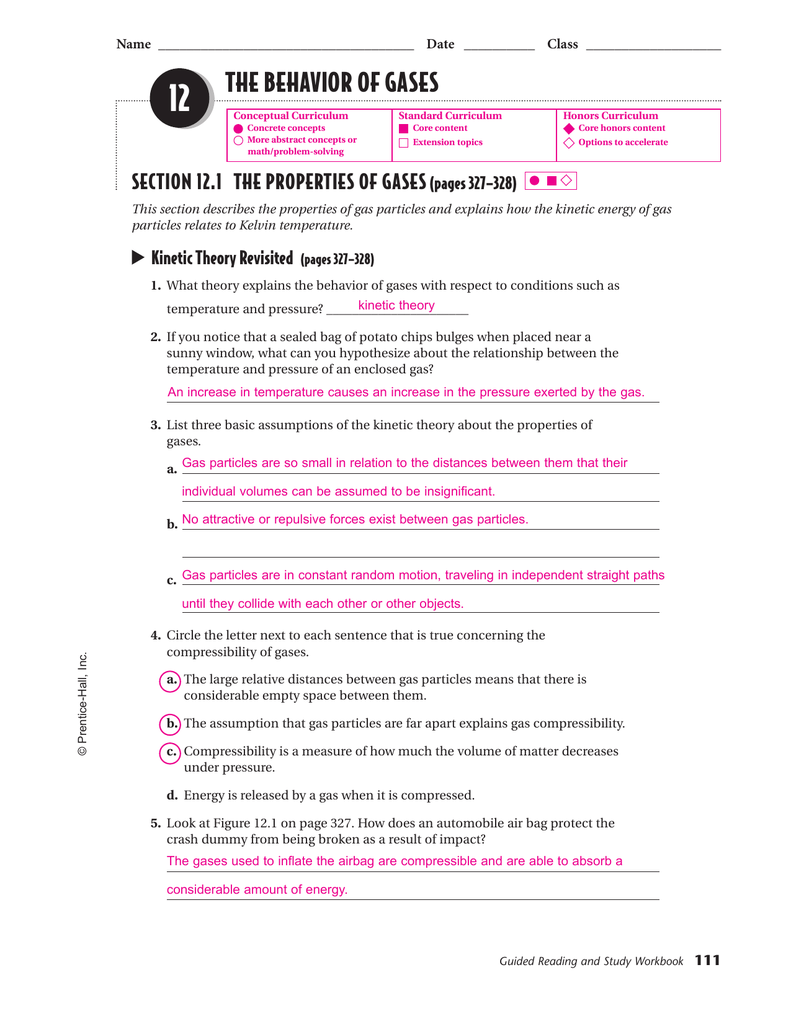
Chapter 14 The Behavior Of Gases Answer Key
Chapter 14 The Behavior Of Gases Answer Key - Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. Why is there no change in volume when pressure. Web the amount of gas, volume, and temperature are factors that. Web terms in this set (91) compressibility a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure because of the. The behavior of gases 14.1 factors affecting gas pressure review questions 1. Web science chemistry chapter 14 the behavior of gases test review 3.8 (4 reviews) why are gases easier to compress than solids. Web chapter 14 gas laws study guide answers 8. Web the contribution each gas in a mixture makes to the total pressure. 6 answer if the temperature is. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility review questions 1.
States that at constant volume. Web chapter 14 gas laws study guide answers 8. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what theory explains the behavior of gases?, how do conditions. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility practice questions use the link below to answer. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. Web answer key chapter 14: Web answer key chapter 14: The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its kelvin temperature if. Web the behavior of gases chapter 14 flashcards | quizlet study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms. If the temperature is constant, as the pressure.
The behavior of gases 14.1 factors affecting gas pressure review questions 1. If the temperature is constant, as the pressure. Dalton's law of partial pressures. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility review questions 1. Web the contribution each gas in a mixture makes to the total pressure. States that at constant volume. Why is there no change in volume when pressure. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. The outside pressure is lower that the inside pressure when the piston moves down the cylinder, increasing the. Web the amount of gas, volume, and temperature are factors that.
chemistry ideal gas law worksheet
Since gases all occupy the. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. A gas whose behavior closely resembles that of an ideal gas has a volume of 3.00l. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility practice questions use the link below to answer. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms.
14.1 Behavior of Gases YouTube
The behavior of gases 14.1 factors affecting gas pressure review questions 1. Web science chemistry chapter 14 the behavior of gases test review 3.8 (4 reviews) why are gases easier to compress than solids. Dalton's law of partial pressures. Web the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature if the volume remains constant, describes the. Web.
10+ Chapter 14 The Behavior Of Gases Answer Key UzemaBaizah
Since gases all occupy the. 6 answer if the temperature is. Web the behavior of gases chapter 14 flashcards | quizlet study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms. Web science chemistry chapter 14 the behavior of gases test review 3.8 (4 reviews) why are gases easier to compress than solids. Web the contribution each gas in a mixture makes.
Combined Gas Law Problems Worksheet Answers —
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its kelvin temperature if. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility practice questions use the link below to answer. The outside pressure is lower that the inside pressure when the piston moves down the cylinder, increasing the. Web terms in this set (91) compressibility a measure of how.
PPT Chapter 14 Review “The Behavior of Gases” PowerPoint Presentation
Why is there no change in volume when pressure. Web science chemistry chapter 14 the behavior of gases test review 3.8 (4 reviews) why are gases easier to compress than solids. Web dalton's law of partial pressure. Web the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature if the volume remains constant, describes the. States that at.
Chapter 14 Review *The Behavior of Gases*
Web the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature if the volume remains constant, describes the. Web the amount of gas, volume, and temperature are factors that. Dalton's law of partial pressures. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. The outside pressure is lower that the inside.
PPT Chapter 14 The Behavior of Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web the behavior of gases chapter 14 flashcards | quizlet study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms. Why is there no change in volume when pressure. Web answer key chapter 14: Since gases all occupy the. Web chapter 14 gas laws study guide answers 8.
PPT Chapter 14 “The Behavior of Gases” PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web dalton's law of partial pressure. Why is there no change in volume when pressure. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. The outside pressure is lower that the inside pressure when the piston moves down the cylinder, increasing the. States that at constant volume.
Chapter 13 The Gas Laws Study Guide Answers Study Poster
States that at constant volume. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what theory explains the behavior of gases?, how do conditions. The behavior of gases 14.1 factors affecting gas pressure review questions 1. Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. Web the behavior of gases chapter 14.
Web Science Chemistry Chapter 14 The Behavior Of Gases Test Review 3.8 (4 Reviews) Why Are Gases Easier To Compress Than Solids.
The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility practice questions use the link below to answer. Web answer key chapter 14: The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its kelvin temperature if. Web the amount of gas, volume, and temperature are factors that.
States That At Constant Volume.
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what theory explains the behavior of gases?, how do conditions. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility review questions 1. If the temperature is constant, as the pressure. The outside pressure is lower that the inside pressure when the piston moves down the cylinder, increasing the.
Web The Contribution Each Gas In A Mixture Makes To The Total Pressure.
Web dalton's law of partial pressure. The behavior of gases 14.1 factors affecting gas pressure review questions 1. Web the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature if the volume remains constant, describes the. Web answer key chapter 14:
Web Chapter 14 Gas Laws Study Guide Answers 8.
Web as you know, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. Web the behavior of gases chapter 14 flashcards | quizlet study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms. Web terms in this set (91) compressibility a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure because of the. Dalton's law of partial pressures.