Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Review Questions Answers
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Review Questions Answers - This is an example of a necessary life function. Study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. Whenever we look at our own body or study large body structures such as the heart or. Given these levels of organization: Even though cells are microscopic, they can vary in the sizes just as atoms do. 13 answer five external factors that must be present or provided to sustain life include: Web answer brachial work step by step brachial refers to the arm, from the latin word brachium, meaning arm. An orientation for this assignment, please read the chapter and answer the questions below. 1 answer the six levels of structural organization of the human body are chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organismal levels. Answer choices regional systemic microscopic homeostatic question 2 120 seconds q.
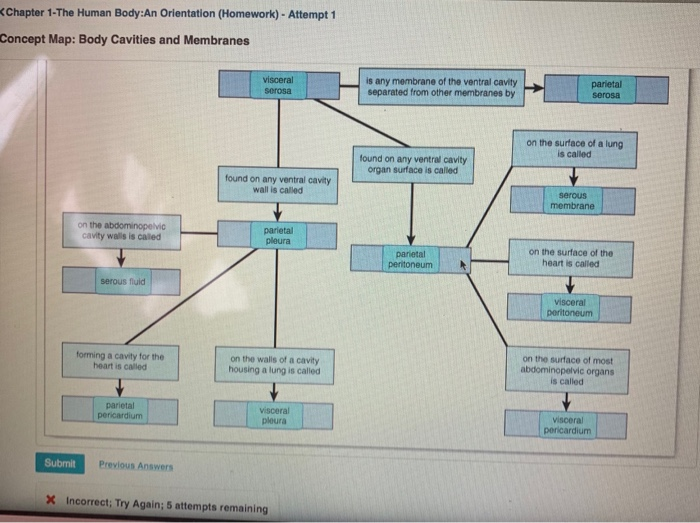
Building blocks of matter, combine to form molecules. Is an increase in size of a body. You can help us out by revising, improving and updating this answer. Describe the serous membranes of the body. Human structure and function (hbs109) s when the body is erect with the f allel and the arms hanging at the sides with the d, with thumbs pointing a rdless of the position the body. An orientation for this assignment, please read the chapter and answer the questions below. An orientation (chapter practice test) which of the following best defines physiology? Is a broad term that includes all chemical reactions that occur w/in body cells. 13 answer five external factors that must be present or provided to sustain life include: 11 answer according to the principle of complementarity, anatomy relates to physiology because structure is related to.
Update this answer after you claim an answer. An orientation 1 matching questions figure 1. Study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. Choose the arrangement that lists the levels of organization in the. 1 answer the six levels of structural organization of the human body are chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organismal levels. Select the correct function from. Web answer cells are the building stones on which every living organism requires. If it were a positive feedback system, we would become even more thirsty as we drink lipids. Web the human body as a whole is enclosed and protected by the integumentary system. Human structure and function (hbs109) s when the body is erect with the f allel and the arms hanging at the sides with the d, with thumbs pointing a rdless of the position the body.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Answers Islero Guide Answer
You can help us out by revising, improving and updating this answer. Web anatomy and physiology questions and answers; Occurs at the cellular and organismal level. 11 answer according to the principle of complementarity, anatomy relates to physiology because structure is related to. Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
An orientation 1 matching questions figure 1. An orientation list and describe the 6 levels of structural organization from least to most complex. Which of the following is not a discipline of anatomy? Study of structures visible to the eye. If it were a positive feedback system, we would become even more thirsty as we drink lipids.
Solved Chapter 2 Orientation to the Human Body The
Whenever we look at our own body or study large body structures such as the heart or. Web all chemical reactions within the body, production of energy, making body structures. Human structure and function (hbs109) s when the body is erect with the f allel and the arms hanging at the sides with the d, with thumbs pointing a rdless.
1000+ images about Medical Terminology on Pinterest Real estate exam
You can help us out by revising, improving and updating this answer. Study of structures visible to the eye. Even though cells are microscopic, they can vary in the sizes just as atoms do. This is an example of a necessary life function. An orientation list and describe the 6 levels of structural organization from least to most complex.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
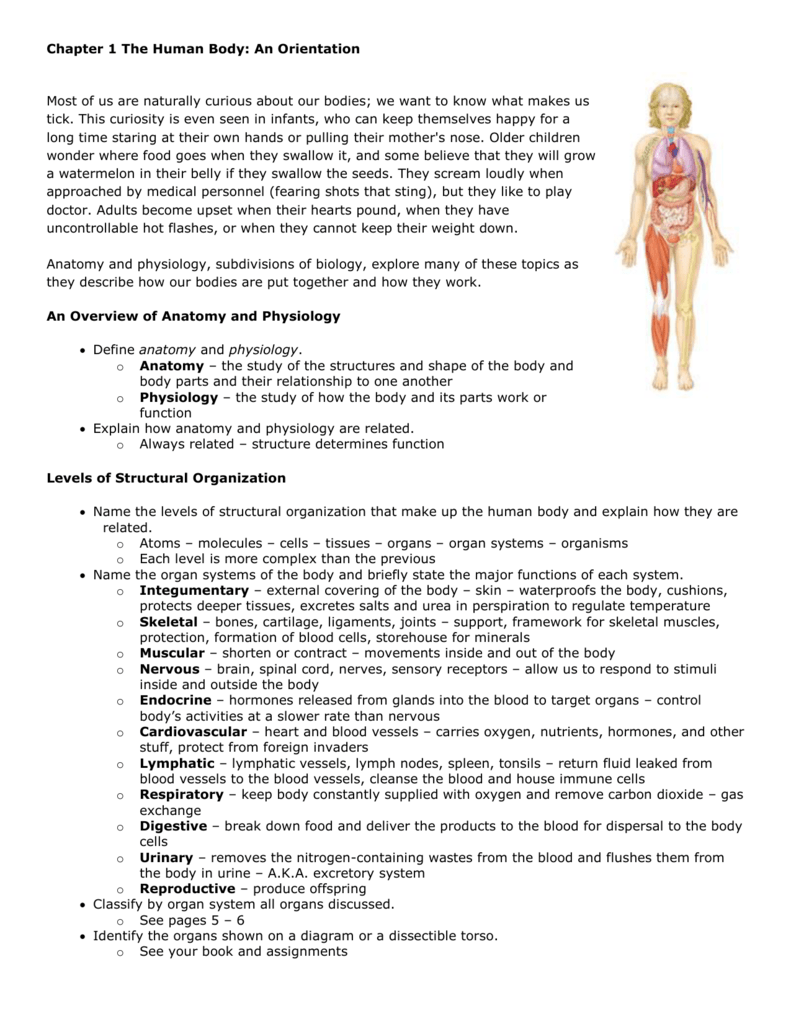
Web the human body as a whole is enclosed and protected by the integumentary system. Web biology anatomy chapter 1: Choose the arrangement that lists the levels of organization in the. Update this answer after you claim an answer. Is the process of removing wastes from the body.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Answer Key RajaLenore
Web answer cells are the building stones on which every living organism requires. Human structure and function (hbs109) s when the body is erect with the f allel and the arms hanging at the sides with the d, with thumbs pointing a rdless of the position the body. An orientation (chapter practice test) which of the following best defines physiology?.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Test Answers SaputraPuri
Web the human body as a whole is enclosed and protected by the integumentary system. Even though cells are microscopic, they can vary in the sizes just as atoms do. 11 answer according to the principle of complementarity, anatomy relates to physiology because structure is related to. Web 1)chemical 2)cellular 3)tissue 4)organ 5)organ system 6)organismal homeostasis existence of stable and.
PPT CHAPTER 1 The Human Body An Orientation PowerPoint Presentation
Building blocks of matter, combine to form molecules. An orientation list and describe the 6 levels of structural organization from least to most complex. Study of structures visible to the eye. Select the correct function from. Web answer brachial work step by step brachial refers to the arm, from the latin word brachium, meaning arm.
Body orientation and direction Anatomy and physiology, Human body, Body
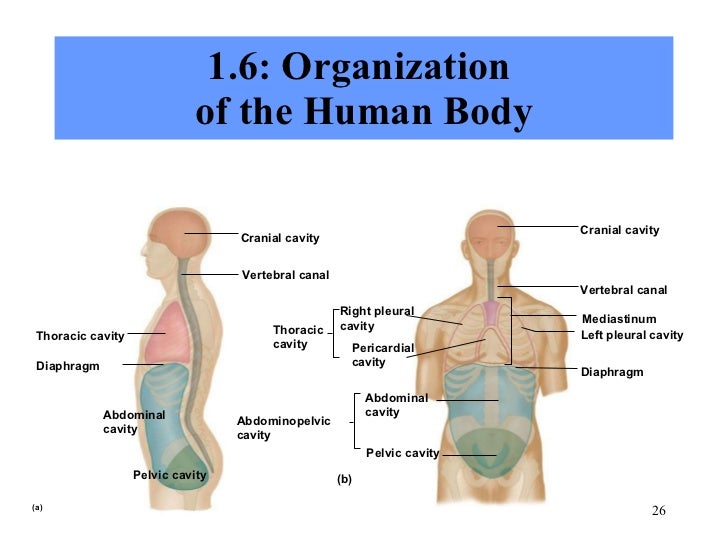
Study of structures visible to the eye. Select the correct function from. 13 answer five external factors that must be present or provided to sustain life include: Study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. Describe the serous membranes of the body.
Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation Worksheet Answers
Web study of the function of the body's parts. Update this answer after you claim an answer. Web anatomy and physiology questions and answers; An orientation for this assignment, please read the chapter and answer the questions below. 11 answer according to the principle of complementarity, anatomy relates to physiology because structure is related to.
You Can Help Us Out By Revising, Improving And Updating This Answer.
Study of structures visible to the eye. Human structure and function (hbs109) s when the body is erect with the f allel and the arms hanging at the sides with the d, with thumbs pointing a rdless of the position the body. An orientation (chapter practice test) which of the following best defines physiology? Select the correct function from.
Whenever We Look At Our Own Body Or Study Large Body Structures Such As The Heart Or.
Cells are what keeps the human body in its form. Which of the following is not a discipline of anatomy? Please note that points may be deducted if answers are not submitted in these colors. An orientation for this assignment, please read the chapter and answer the questions below.
Is A Broad Term That Includes All Chemical Reactions That Occur W/In Body Cells.
In a negative feedback mechanism answer choices the effect damages the body… Web answer cells are the building stones on which every living organism requires. Web all chemical reactions within the body, production of energy, making body structures. Web enables the body to be able to detect changes in the surrounding environment and then respond to changes.
1 Answer The Six Levels Of Structural Organization Of The Human Body Are Chemical, Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, And Organismal Levels.
Levels of structural organization (6) atomic, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism. Please type your answers in red or blue color. An orientation list and describe the 6 levels of structural organization from least to most complex. Web study of the function of the body's parts.